|
World Database of NematodesLinked to the Marine Biology Section, UGent |
| Start | Browse taxonomy |
Search taxonomy |
Search literature |
Search distributions |
Identification keys |
Media gallery | Editors | Statistics | Citations | Match taxa | Contact | Login |
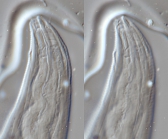
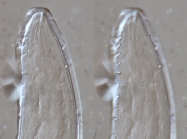
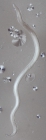
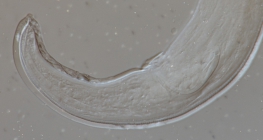
Nemys taxon detailsDeontolaimus de Man, 1880
2394 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:2394)
accepted
Genus
Acontiolaimus Filipjev, 1918 · unaccepted (synonym)
Camacolaimoides De Coninck & Schuurmans Stekhoven, 1933 · unaccepted (synonym)
Camacolaimus de Man, 1889 · unaccepted (synonym)
Digitonchus Cobb, 1920 · unaccepted (synonym)
Ypsilon Cobb, 1920 · unaccepted (synonym)
marine, brackish,
recent only
De Man, J. G. (1879). Die Einheimischen, Frei In Der Reinen Erde Und Im Süssen Wasser Lebenden Nematoden. Monographisch Bearbeitet. Vorläufiger Bericht und descriptiv-systematischer Theil. Tijdschrift der Nederlandsche Dierkundige Vereeniging. 5: 1-104. (look up in IMIS) [details]
Taxonomy The genus Deontolaimus de Man, 1880 was revised and the genus Camacolaimus de Man, 1889 is considered a junior synonym of...
Taxonomy The genus Deontolaimus de Man, 1880 was revised and the genus Camacolaimus de Man, 1889 is considered a junior synonym of Deontolaimus based on re-examination of type material of Camacolaimus tardus de Man, 1889 and C. barbatus Warwick, 1970. [details]
Nemys eds. (2024). Nemys: World Database of Nematodes. Deontolaimus de Man, 1880. Accessed at: https://nemys.ugent.be/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=2394 on 2025-04-04
Date action by 2004-12-21 15:54:05Z created db_admin 2006-07-31 06:57:06Z changed Camba Reu, Cibran
original description
De Man, J. G. (1879). Die Einheimischen, Frei In Der Reinen Erde Und Im Süssen Wasser Lebenden Nematoden. Monographisch Bearbeitet. Vorläufiger Bericht und descriptiv-systematischer Theil. Tijdschrift der Nederlandsche Dierkundige Vereeniging. 5: 1-104. (look up in IMIS) [details]
original description (of Acontiolaimus Filipjev, 1918) Filipjev, I. N. (1918). Free-living marine nematodes of the Sevastopol area. Transactions of the Zoological Laboratory and the Sevastopol Biological Station of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Series II No 4 (Issue I & II) (Translated from Russian). [details] original description (of Digitonchus Cobb, 1920) Cobb, N. A. (1920). One hundred new nemas (type species of 100 new genera). Contributions to a science of nematology. 9: 217-343., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/18212644 [details] original description (of Ypsilon Cobb, 1920) Cobb, N. A. (1920). One hundred new nemas (type species of 100 new genera). Contributions to a science of nematology. 9: 217-343., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/18212644 [details] original description (of Camacolaimoides De Coninck & Schuurmans Stekhoven, 1933) Schuurmans Stekhoven, J. H. Jr.; De Coninck, L. A. (1933). Morphologische Fragen zur Systematik der freleibenden Nematoden. Verhandl. der Deutschen Zoolog. Gesellschaft. 138-143. [details] Available for editors original description (of Camacolaimus de Man, 1889) de Man, J. G. (1889). Espèces et genres nouveaux de Nématodes libres de la mer du Nord et de la Manche. Mém. Soc. zool. Fr. 2: 1-10., available online at http://biostor.org/reference/61320 page(s): 8 [details] taxonomy source Holovachov, O.; Boström, S. (2015). Swedish Plectida (Nematoda). Part 10. The genus Deontolaimus de Man, 1880. Zootaxa. 4034(1): 1., available online at https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4034.1.1 [details] Available for editors basis of record Nemaslan: Biodiversity of Antarctic Nematodes (2004). (look up in IMIS) [details] additional source Neave, Sheffield Airey. (1939-1996). Nomenclator Zoologicus vol. 1-10 Online. [Online Nomenclator Zoologicus at Checklistbank. Ubio link has gone]. , available online at https://www.checklistbank.org/dataset/126539/about [details] additional source Timm, R. W. (1957). New Marine Nematodes from St. Martin's Island. Pakist. J. Scient. Res., 9 (4): 133-138 [details] Available for editors additional source Maria, T. F.; Esteves, A. M.; Smol, N.; Vanreusel, A.; Decraemer, W. (2008). Nematodes from sandy beaches of Guanabara Bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Biociências, Porto Alegre. 16 (2), 92-103. [details] Available for editors additional source Venekey, V.; Fonseca-Genevois, V.; Santos, P. J. P. (2010). Biodiversity of free-living marine nematodes on the coast of Brazil: a review. Zootaxa. 2568: 39–66. [details] Available for editors  Present Present  Inaccurate Inaccurate  Introduced: alien Introduced: alien  Containing type locality Containing type locality
From editor or global species database
Taxonomy The genus Deontolaimus de Man, 1880 was revised and the genus Camacolaimus de Man, 1889 is considered a junior synonym of Deontolaimus based on re-examination of type material of Camacolaimus tardus de Man, 1889 and C. barbatus Warwick, 1970. [details]
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Camacolaimus) (from synonym Camacolaimus de Man, 1889)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Deontolaimus) To Genbank (from synonym Camacolaimus de Man, 1889) To Genbank To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Nematoda Collection (1 record) To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Nematoda Collection (1 record) (from synonym Camacolaimoides De Coninck & Schuurmans Stekhoven, 1933) To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Nematoda Collection (10 records) (from synonym Camacolaimus de Man, 1889) To ITIS |
Web interface and database structure initially created by Tim Deprez; now hosted and maintained by VLIZ
Page generated 2025-04-04 · contact: Tânia Nara Bezerra or info@marinespecies.org